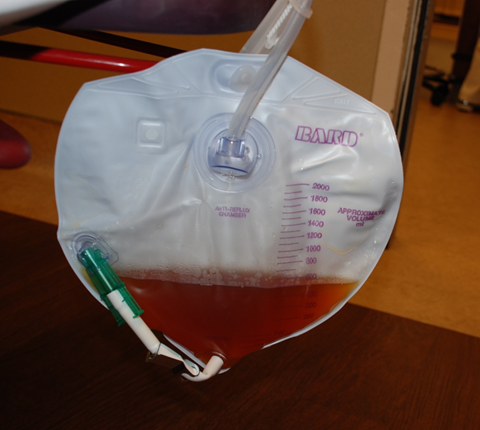
Soft Tissue Case 10 Background
Rhabdomyolysis is the destruction of skeletal muscle and the release of intracellular constituents into the circulation. It is caused by any mechanism that results in injury to myocytes including:
- Trauma (usually crush injury)
- Prolonged immobilization (such as passing out while intoxicated)
- Exertion from strenuous exercise, seizure, or agitation
- Substances such as statins, colchicine, cocaine, amphetamines, PCP
- Infection from viral or bacterial myositis
- Inflammatory myopathies
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypophosphatemia
- Hyperthermia
The extensive release of intracellular contents can result in acute kidney injury and severe fluid and electrolyte abnormalities such as: hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperuricemia.
Other potential complications include compartment syndrome, which usually occurs after treatment with aggressive fluids, as well as disseminated intravascular coagulation.